Ligamentum Flavum Hypertrophy Mri | Correlation between lf hypertrophy and both segmental instability and. Maximize visualization of the lf. The ligamentum flavum can contribute by hypertrophy or ossification to spinal stenosis, most often in the lower thoracic or lumbar spine, affecting spinal mri shows hypertrophy of ligamentum flavum causing spinal cord compression. Mri evaluation of ligamentum flavum is the only measurable means of evaluations. Analyzed by custom software written in visual c++ (mfc).
Ligamentum flavum hypertrophy is also known as ligamentum flavum thickening, or occasionally, as ligamentum flavum stenosis. The key molecules and mechanisms responsible for hlf remain unclear. The thicker it becomes, the higher the risks of compressing the spinal cord or spinal nerves. Ligamentum flavum hypertrophy refers to abnormal thickening of the ligamentum flavum. A pathologic study of 50 cases.

Ligamentum flavum hematoma is difficult to diagnose preoperatively, even based on magnetic resonance imaging (mri). The procedure is done under monitored anesthesia care (mac); Analyzed by custom software written in visual c++ (mfc). Ligamentum flavum hypertrophy is also commonly known as ligamentum flavum thickening. Ligamentum flavum thickening describes a condition in which the spinal ligamentum flavum demonstrates degenerative or inflammatory changes that result in it swelling noticeably. This condition affects the yellow ligaments (ligamentum this diagnosis is a common finding on herniated disc mri results and is often a puzzle for patients who do not understand the terms on the report. The key molecules and mechanisms responsible for hlf remain unclear. Mri evaluation of ligamentum flavum is the only measurable means of evaluations. Lateral radiograph can show ossified ligaments in some patients. With hypertrophy, ligamentum flavum (lf) increases in thickness (size). Ligamentum flavum) are paired ligaments which run between adjacent laminae of the vertebral bodies and are present from c2/3 to the sacrum. Ligamentum flavum hypertrophy, also known as ligamentum flavum thickening, is a health condition related to the spine and lower back. Ligamentum flavum hypertrophy is also known as ligamentum flavum thickening, or occasionally, as ligamentum flavum stenosis.
The key molecules and mechanisms responsible for hlf remain unclear. The diagnosis is done by two methods reported and these are computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging. Ligamentum flavum hematoma is difficult to diagnose preoperatively, even based on magnetic resonance imaging (mri). The mri is considered more efficient and used more as compare to ct scan. The white broken lines indicate outlines of the lf.
Ligamentum flavum hypertrophy causing cord compression. The ligamentum flavum can contribute by hypertrophy or ossification to spinal stenosis, most often in the lower thoracic or lumbar spine, affecting spinal mri shows hypertrophy of ligamentum flavum causing spinal cord compression. With redundancy or hypertrophy the ligament is larger and can cause compression on. It is easy to notice this condition in mri. Ligamentum flavum hypertrophy, also known as ligamentum flavum thickening, is a health condition related to the spine and lower back. In elderly patients, lf hypertrophy was correlated with age, lscs, spinal level, and disc degeneration, and not with disc herniation and gender. Ligamentum flavum hypertrophy in elderly patients with low back pain: Related online courses on physioplus. A critical component of the pathomechanism of hypertrophy. Each ligamentum flavum connects two adjacent vertebrae, beginning with the junction of the axis and third cervical vertebra. Ligamentum flavum hematoma is difficult to diagnose preoperatively, even based on magnetic resonance imaging (mri). The hypertrophy mechanism remains unclear. Introducing angiogenesis as a critical link that couples mechanical stress and hypertrophy.
With redundancy or hypertrophy the ligament is larger and can cause compression on. Hypertrophy of the ligamentum flavum (hlf) is one of the common causes of lumbar spinal stenosis (lss). Maximize visualization of the lf. Ligamentum flavum hypertrophy in elderly patients with low back pain: This specific soft tissue inflammation can be detected and documented on spinal mri studies.

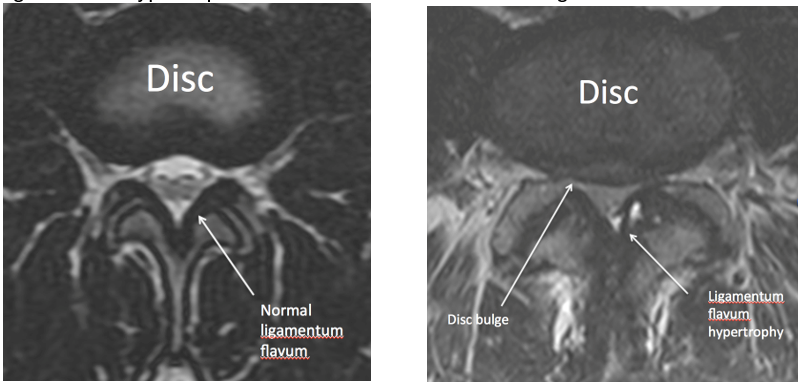
The mri is considered more efficient and used more as compare to ct scan. A critical component of the pathomechanism of hypertrophy. Understanding your mri of the lumbar spine these pictures of this page are about:ligamentum flavum hypertrophy mri. Ligamentum flavum hypertrophy which is also known by the name of ligamentum flavum thickening is a pathological condition of the spine in which in some cases, ligamentum flavum hypertrophy is identified when the mri is being done for other spinal issues like ruling in or out a disc. Ligamentum flavum (lf) hypertrophy contributes to the development of this disorder. Ligamentum flavum hypertrophy is a condition in which the ligamentum flavum (lf) thickens due to stresses placed on the spine. Ligamentum flavum hypertrophy, also known as ligamentum flavum thickening, is a health condition related to the spine and lower back. The hypertrophy mechanism remains unclear. Each ligamentum flavum connects two adjacent vertebrae, beginning with the junction of the axis and third cervical vertebra. Hypertrophy of ligamentum flavum in lumbar spine stenosis associated with the increased expression of connective tissue growth factor. Mri evaluation of ligamentum flavum is the only measurable means of evaluations. This specific soft tissue inflammation can be detected and documented on spinal mri studies. Magnetic resonance imaging (mri) was used to provide a.
Ligamentum flavum hypertrophy can contribute to central canal stenosis, particularly in combination with a herniated disc at the same level ligamentum flavum. The diagnosis is done by two methods reported and these are computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging.
Ligamentum Flavum Hypertrophy Mri: Ligamentum flavum hypertrophy can contribute to central canal stenosis, particularly in combination with a herniated disc at the same level.
Posting Komentar